
Alternately, corners can be insulated with suitable insulation before the drywall or plasterboard is installed. Check with window manufacturer for approved sealing procedures and materials.Ħ.1.4 Insulating the corners of attics in buildings with hip roofs may require special nozzles or placement tools. Note 1 - Some window manufacturers will not honor warranties if foam is used, even if the foam is non-expanding. Various materials such as foam backer rod or urethane spray foam are available for this purpose.
Installing rafter vents diagram windows#
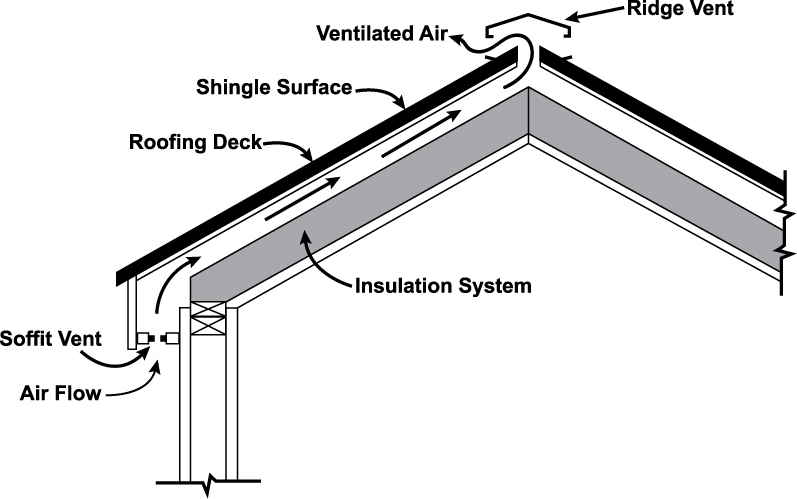
1A and 1B).Ħ.1.3 All voids around windows and doors should be sealed to stop air infiltration. Other spaces should be totally blocked.Ħ.1.2 Where a continuous strip vent is used in the soffit, an air chute should be provided in every rafter space (see Fig. (See Sections 9 and 10 for some of the steps to be taken.)Ħ.1.1 Where individual vents are used in the soffit, the rafter space immediately in front of and on either side of the vent should be provided with an air chute (see Fig.1A and Fig. Insulation alone may not solve such problems. Special consideration should be given to the following areas.ĥ.2.1 Holes in ceilings or sidewalls, that would allow the insulation to escape, should be sealed.ĥ.2.2 Weak areas of interior walls that may not be able to withstand pressures during the filling operation should be reinforced.ĥ.2.3 Walls with alterations, such as built-in bookshelves and cabinets, which create isolated cavities, will require special entry holes.ĥ.2.4 Wall cavities, which are used as air ducts for heating or air conditioning systems, must not be filled with insulation.ĥ.2.5 Openings in heating or air conditioning air systems, in insulated areas, must have blocking placed around them.ĥ.2.6 Wall cavities, which open into basements or crawl spaces, must be sealed.ĥ.2.7 The external siding of existing buildings should be inspected for paint peeling or other evidence of moisture problems.

Any surfaces or substrates that are wet, damaged or have any signs of mold should not be insulated until these problems are corrected. A moisture meter is recommended when installing stabilized cellulose insulation in both new and existing sidewalls.ĥ.2 The installing contractor shall examine all surfaces and substrates to be installed upon and ensure that they are in a suitable state.

A thermal camera and other inspection / diagnostic tools are recommended for before and after installation inspections when applying insulation in existing building. It must have sufficient strength to withstand the pressure developed when filling the cavity.Ĥ.2 Blocking - a material used to retain the insulation in place in open areas.Ĥ.3 Fill tube - a tube which enables a cavity to be filled through a single entry hole.Ĥ.4 Enclosed ceiling cavities - a ceiling area which is covered on both top and bottom.ĥ.1 An inspection of the building shall be made prior to installation. which is used to cover the open side of an existing wall and forms a cavity which may be filled with loose fill insulation. It also identifies some of the precautions which need to be taken.Ĭ-168 Standard Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulating MaterialsĬ-739 Standard Specification for Cellulosic Fiber (Wood Base) Loose Fill Thermal InsulationĬ-755 Standard Practice for Selection of Vapor retarders for Thermal Insulation C-1149 Standard Specification for Self-Supported Spray Applied Cellulosic Thermal / Acoustical InsulationĬ-1015 Standard Practice for Installation of Cellulosic and Mineral Fiber Loose-Fill Thermal InsulationĮ-241 Standard Guide for Limiting Water-Induced Damage to Buildingsġ6 CFR Part 1209 Consumer Products Safety Commission Interim Safety Standard for Cellulose Insulationġ6 CFR Part 460 FTC Trade Regulation Rule, Labeling and Advertising of Home InsulationĤ.1 Backer board - a rigid, non vapor barrier forming material such as rock lath, treated cardboard, plywood, netting, etc. The purpose of this recommended practice is to inform installers, system designers and consumers of acceptable procedures to ensure proper installation. This recommended practice covers the application of cellulosic thermal insulation in attics, sidewall cavities and between floors of single & multi family dwellings and other buildings by means of pneumatic equipment. This guide covers typical assembly designs and some of the more common installation methods that can be used to insulate new and existing structures. Cellulose insulation can be installed in attics, walls, ceilings, floors, and other building assemblies using a variety of standard accepted techniques.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
